There are a few basic factors to consider when choosing your inverter capacity. Choosing the right inverter capacity is important for the inverter to be able to operate the connected devices efficiently and for the system to be safe. Here are the main factors to consider when choosing your inverter capacity:
1. Total Power Consumption (Watt):
Power Consumption of Devices: You should determine the power (in Watts) of all the devices you plan to use. The power consumption of each device is usually indicated on the device.
2. Start-up Power (Surge Power):
Start-up Power of Devices: Some devices, especially motorized devices (refrigerator, air conditioner, water pump, etc.), draw more energy than their normal operating power when they start working. This “start-up power” (or instantaneous peak power) can usually be 2-3 times the nominal power.
For example, a 300W refrigerator can draw up to 900W of energy when starting up.
Instantaneous Power Capacity of the Inverter: When choosing an inverter, you should also consider the starting power of the devices. The inverter needs to be capable of handling these temporary high power demands.
Example:
Let’s say you plan to run the following devices in your home simultaneously:
Television: 150W
Laptop: 100W
Refrigerator: 400W (initially 1000W)
Lighting: 100W
In this case:
Total continuous power: 150W + 100W + 400W + 100W = 750W
Start-up power: 1200W (for the refrigerator)
Since you have a continuous power requirement of 750W, it would be appropriate to choose an inverter with a capacity of at least 1500W to meet the starting power.
 Havale/EFT ile %5 anında indirim!
Havale/EFT ile %5 anında indirim!





























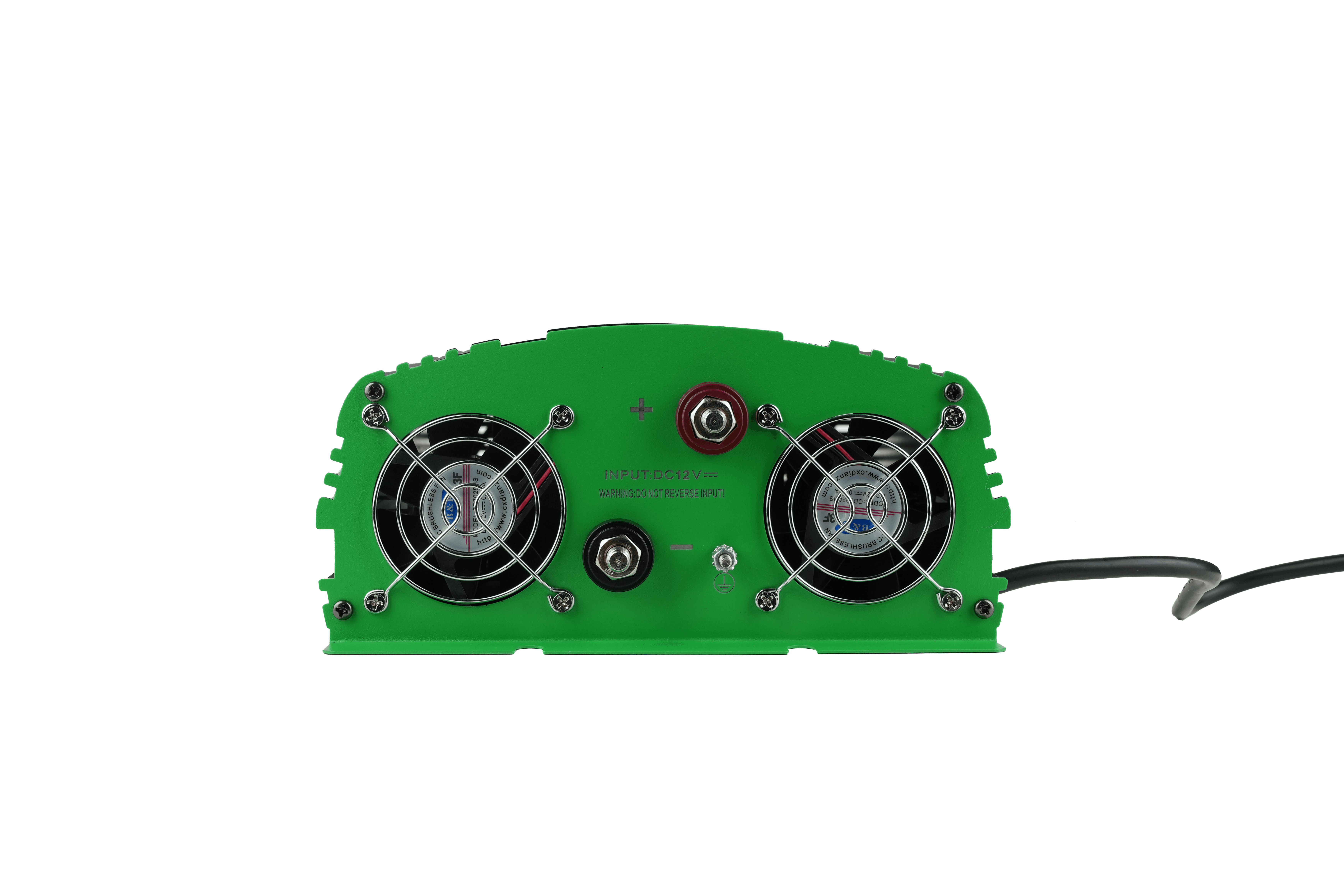
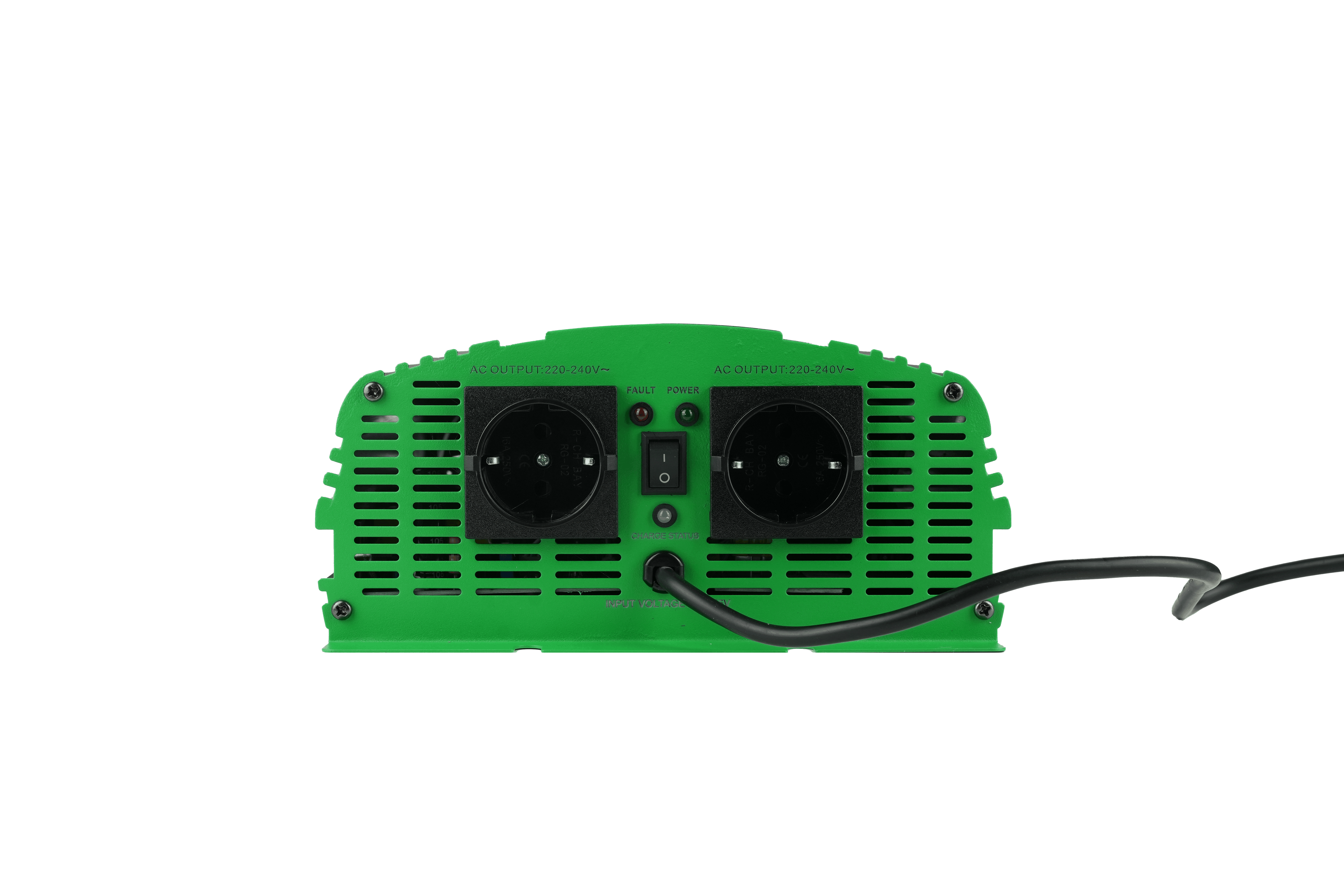





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.